Home
| About
| Mine Tracker
| RSS
| Footer
▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄ █▄▄░▄▄█░▄▄▀█░▄▄▀█▀▄▀█░▄▄███░▄▄▀█░▄▄▀█░▄▀███▄▄░▄▄█░▄▄▀█░▄▄▀█▀▄▀█░▄▄█░▄▄▀█░▄▄▀██▄██░███▄██▄░▄█░██░ ███░███░▀▀▄█░▀▀░█░█▀█░▄▄███░▀▀░█░██░█░█░█████░███░▀▀▄█░▀▀░█░█▀█░▄▄█░▀▀░█░▄▄▀██░▄█░███░▄██░██░▀▀░ ███░███▄█▄▄█▄██▄██▄██▄▄▄███▄██▄█▄██▄█▄▄██████░███▄█▄▄█▄██▄██▄██▄▄▄█▄██▄█▄▄▄▄█▄▄▄█▄▄█▄▄▄██▄██▀▀▀▄ ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
Supply Chain Alternatives if Climate Change-driven Water Shortages Persist at the Panama Canal
https://www.bakerinstitute.org/research/supply-chain-alternatives-ocean-shipping-if-climate-change-driven-water-shortages-persist
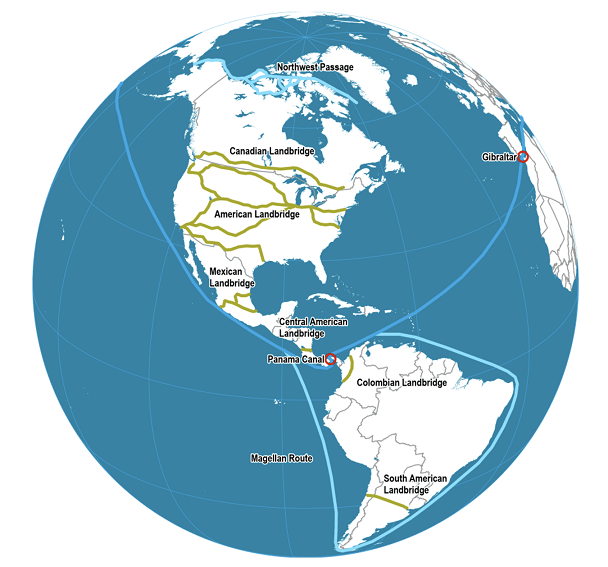
A severe drought is currently affecting the Panama Canal and, exacerbated by the weather pattern known as El Niño, water shortages are likely to persist well into 2024. For each ship transiting the canal, approximately 52 million gallons of water are needed to operate the sets of locks ascending from the Pacific Ocean toward Gatun Lake in Panama (the highest point of the canal at 85 feet above sea level) and descending again to sea level on the Atlantic Ocean side. The water required comes from Gatun Lake, an artificial lake built to service the canal, and other smaller sources. Because the drought has lowered lake water levels, a depth limit of 44 feet — 4 to 5 feet lower than normal — has been imposed on ships transiting the canal, and daily crossings have been reduced from 36 to 32, contributing to a backlog of 264 ships as of mid-August.
https://www.bakerinstitute.org/research/supply-chain-alternatives-ocean-shipping-if-climate-change-driven-water-shortages-persist

A severe drought is currently affecting the Panama Canal and, exacerbated by the weather pattern known as El Niño, water shortages are likely to persist well into 2024. For each ship transiting the canal, approximately 52 million gallons of water are needed to operate the sets of locks ascending from the Pacific Ocean toward Gatun Lake in Panama (the highest point of the canal at 85 feet above sea level) and descending again to sea level on the Atlantic Ocean side. The water required comes from Gatun Lake, an artificial lake built to service the canal, and other smaller sources. Because the drought has lowered lake water levels, a depth limit of 44 feet — 4 to 5 feet lower than normal — has been imposed on ships transiting the canal, and daily crossings have been reduced from 36 to 32, contributing to a backlog of 264 ships as of mid-August.