Home
| About
| Mine Tracker
| RSS
| Footer
▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄ █▄▄░▄▄█░▄▄▀█░▄▄▀█▀▄▀█░▄▄███░▄▄▀█░▄▄▀█░▄▀███▄▄░▄▄█░▄▄▀█░▄▄▀█▀▄▀█░▄▄█░▄▄▀█░▄▄▀██▄██░███▄██▄░▄█░██░ ███░███░▀▀▄█░▀▀░█░█▀█░▄▄███░▀▀░█░██░█░█░█████░███░▀▀▄█░▀▀░█░█▀█░▄▄█░▀▀░█░▄▄▀██░▄█░███░▄██░██░▀▀░ ███░███▄█▄▄█▄██▄██▄██▄▄▄███▄██▄█▄██▄█▄▄██████░███▄█▄▄█▄██▄██▄██▄▄▄█▄██▄█▄▄▄▄█▄▄▄█▄▄█▄▄▄██▄██▀▀▀▄ ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
Wikipedia; FPIC
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Free,_prior_and_informed_consent
Free, prior and informed consent (FPIC) is aimed to establish bottom-up participation and consultation of an indigenous population prior to the beginning of development on ancestral land or using resources in an indigenous population's territory.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Free,_prior_and_informed_consent
Free, prior and informed consent (FPIC) is aimed to establish bottom-up participation and consultation of an indigenous population prior to the beginning of development on ancestral land or using resources in an indigenous population's territory.
Norman Woodland; Inventor of the barcode
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Norman_Joseph_Woodland
He drew dots and dashes in the sand similar to the shapes used in Morse code. After pulling them downward with his fingers, producing thin lines resulting from the dots and thick lines from the dashes, he came up with the concept of a two-dimensional, linear Morse code.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Norman_Joseph_Woodland
He drew dots and dashes in the sand similar to the shapes used in Morse code. After pulling them downward with his fingers, producing thin lines resulting from the dots and thick lines from the dashes, he came up with the concept of a two-dimensional, linear Morse code.
Our Common Future
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Our_Common_Future
Our Common Future, also known as the Brundtland Report, was published in October 1987 by the United Nations through the Oxford University Press. This publication was in recognition of Gro Harlem Brundtland, former Norwegian Prime Minister and Chair of the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED). Its targets were multilateralism and interdependence of nations in the search for a sustainable development path. The report sought to recapture the spirit of the Stockholm Conference which had introduced environmental concerns to the formal political development sphere. Our Common Future placed environmental issues firmly on the political agenda; it aimed to discuss the environment and development as one single issue.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Our_Common_Future
Our Common Future, also known as the Brundtland Report, was published in October 1987 by the United Nations through the Oxford University Press. This publication was in recognition of Gro Harlem Brundtland, former Norwegian Prime Minister and Chair of the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED). Its targets were multilateralism and interdependence of nations in the search for a sustainable development path. The report sought to recapture the spirit of the Stockholm Conference which had introduced environmental concerns to the formal political development sphere. Our Common Future placed environmental issues firmly on the political agenda; it aimed to discuss the environment and development as one single issue.
Comply or Explain
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comply_or_explain
Rather than setting out binding laws, government regulators (in the UK, the Financial Reporting Council (FRC), in Germany, under the Aktiengesetz) set out a code, which listed companies may either comply with, or if they do not comply, explain publicly why they do not. The purpose of "comply or explain" is to "let the market decide" whether a set of standards is appropriate for individual companies. Since a company may deviate from the standard, this approach rejects the view that "one size fits all", but because of the requirement of disclosure of explanations to market investors, anticipates that if investors do not accept a company's explanations, then they will sell their shares, hence creating a "market sanction", rather than a legal one.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comply_or_explain
Rather than setting out binding laws, government regulators (in the UK, the Financial Reporting Council (FRC), in Germany, under the Aktiengesetz) set out a code, which listed companies may either comply with, or if they do not comply, explain publicly why they do not. The purpose of "comply or explain" is to "let the market decide" whether a set of standards is appropriate for individual companies. Since a company may deviate from the standard, this approach rejects the view that "one size fits all", but because of the requirement of disclosure of explanations to market investors, anticipates that if investors do not accept a company's explanations, then they will sell their shares, hence creating a "market sanction", rather than a legal one.
Beer Game, Supply Chain Game
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beer_distribution_game

The beer distribution game (also known as the beer game) is an educational game that is used to experience typical coordination problems of a supply chain process. It reflects a role-play simulation where several participants play with each other. The game represents a supply chain with a non-coordinated process where problems arise due to lack of information sharing.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beer_distribution_game

The beer distribution game (also known as the beer game) is an educational game that is used to experience typical coordination problems of a supply chain process. It reflects a role-play simulation where several participants play with each other. The game represents a supply chain with a non-coordinated process where problems arise due to lack of information sharing.
Guarantee of origin (GoO)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guarantee_of_origin
A Guarantee of Origin (GO or GoO) is an energy certificate defined in article 15 of the European Directive 2009/28/EC. A GO labels electricity from renewable sources to provide information to electricity customers on the source of their energy. Guarantees of origin are the only precisely defined instruments evidencing the origin of electricity generated from renewable energy sources. In operation, a GO is a green label or tracker that guarantees that one MWh of electricity has been produced from renewable energy sources. Guarantees of origin are traded. When a company buys guarantees of origin, as documentation for the electricity delivered or consumed, the guarantees of origin are cancelled in the electronic certificate registry.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guarantee_of_origin
A Guarantee of Origin (GO or GoO) is an energy certificate defined in article 15 of the European Directive 2009/28/EC. A GO labels electricity from renewable sources to provide information to electricity customers on the source of their energy. Guarantees of origin are the only precisely defined instruments evidencing the origin of electricity generated from renewable energy sources. In operation, a GO is a green label or tracker that guarantees that one MWh of electricity has been produced from renewable energy sources. Guarantees of origin are traded. When a company buys guarantees of origin, as documentation for the electricity delivered or consumed, the guarantees of origin are cancelled in the electronic certificate registry.
AIS, Automatic Identification System
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Automatic_identification_system
The automatic identification system (AIS) is an automatic tracking system that uses transceivers on ships and is used by vessel traffic services (VTS).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Automatic_identification_system
The automatic identification system (AIS) is an automatic tracking system that uses transceivers on ships and is used by vessel traffic services (VTS).
Bullwhip effect
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bullwhip_effect
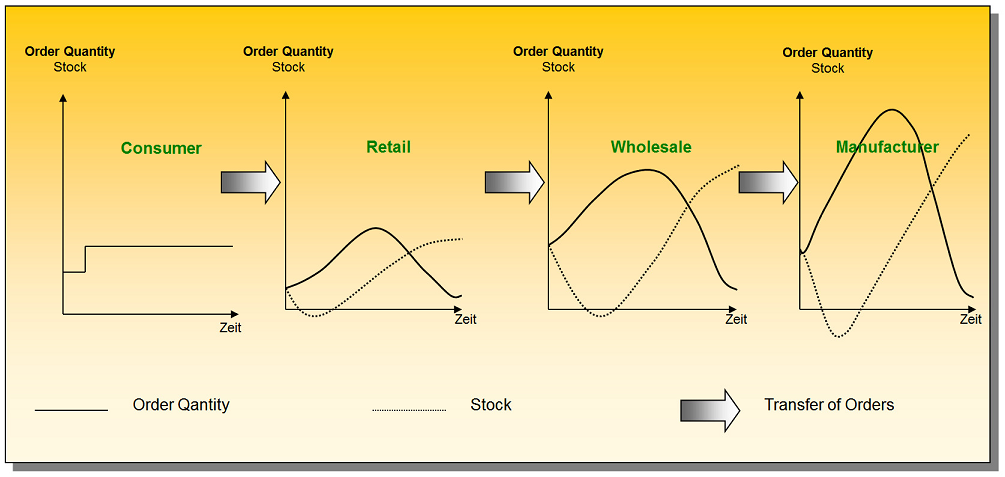
The bullwhip effect is a distribution channel phenomenon in which demand forecasts yield supply chain inefficiencies. It refers to increasing swings in inventory in response to shifts in consumer demand as one moves further up the supply chain. The concept first appeared in Jay Forrester's Industrial Dynamics (1961) and thus it is also known as the Forrester effect. It has been described as “the observed propensity for material orders to be more variable than demand signals and for this variability to increase the further upstream a company is in a supply chain”.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bullwhip_effect

The bullwhip effect is a distribution channel phenomenon in which demand forecasts yield supply chain inefficiencies. It refers to increasing swings in inventory in response to shifts in consumer demand as one moves further up the supply chain. The concept first appeared in Jay Forrester's Industrial Dynamics (1961) and thus it is also known as the Forrester effect. It has been described as “the observed propensity for material orders to be more variable than demand signals and for this variability to increase the further upstream a company is in a supply chain”.
List of busiest container ports (Wikipedia)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_busiest_container_ports
This article lists the world's busiest container ports (ports with container terminals that specialize in handling goods transported in intermodal shipping containers), by total number of twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs) transported through the port. The table lists volume in thousands of TEU per year. The vast majority of containers moved by large, ocean-faring container ships, are 20-foot (1 TEU), and 40-foot (2 TEU) ISO-standard shipping containers, with 40-foot units outnumbering 20-foot units to such an extent, that the actual number of containers moved is between 55%–60% of the number of TEUs counted.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_busiest_container_ports
This article lists the world's busiest container ports (ports with container terminals that specialize in handling goods transported in intermodal shipping containers), by total number of twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs) transported through the port. The table lists volume in thousands of TEU per year. The vast majority of containers moved by large, ocean-faring container ships, are 20-foot (1 TEU), and 40-foot (2 TEU) ISO-standard shipping containers, with 40-foot units outnumbering 20-foot units to such an extent, that the actual number of containers moved is between 55%–60% of the number of TEUs counted.
International Maritime Organization (IMO) number
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IMO_number
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) number is a generic term covering two distinct meanings: the IMO ship identification number, a type of hull number used as a unique ship identifier, and the IMO company and registered owner identification number, used to identify uniquely each company and/or registered owner managing ships of at least 100 gross tons (gt).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IMO_number
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) number is a generic term covering two distinct meanings: the IMO ship identification number, a type of hull number used as a unique ship identifier, and the IMO company and registered owner identification number, used to identify uniquely each company and/or registered owner managing ships of at least 100 gross tons (gt).
Maritime Mobile Service Identity (MMSI)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maritime_Mobile_Service_Identity
A Maritime Mobile Service Identity (MMSI) is effectively a maritime object's international maritime telephone number, a temporarily assigned UID, issued by that object's current flag state, (unlike an IMO, which is a global forever UID).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maritime_Mobile_Service_Identity
A Maritime Mobile Service Identity (MMSI) is effectively a maritime object's international maritime telephone number, a temporarily assigned UID, issued by that object's current flag state, (unlike an IMO, which is a global forever UID).
GEPIR: Global Electronic Party Information Registry, Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GEPIR
The GS1 GEPIR (Global Electronic Party Information Register) is a distributed database that contains basic information on over 1,000,000 companies in over 100 countries. The database can be searched by GTIN code (includes UPC and EAN-13 codes), container Code (SSCC), location number (GLN), and (in some countries) the company name.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GEPIR
The GS1 GEPIR (Global Electronic Party Information Register) is a distributed database that contains basic information on over 1,000,000 companies in over 100 countries. The database can be searched by GTIN code (includes UPC and EAN-13 codes), container Code (SSCC), location number (GLN), and (in some countries) the company name.
Global Trade Item Number (GTIN), Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Global_Trade_Item_Number
The Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) is an identifier for trade items, developed by the international organization GS1. Such identifiers are used to look up product information in a database (often by entering the number through a barcode scanner pointed at an actual product) which may belong to a retailer, manufacturer, collector, researcher, or other entity. The uniqueness and universality of the identifier is useful in establishing which product in one database corresponds to which product in another database, especially across organizational boundaries.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Global_Trade_Item_Number
The Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) is an identifier for trade items, developed by the international organization GS1. Such identifiers are used to look up product information in a database (often by entering the number through a barcode scanner pointed at an actual product) which may belong to a retailer, manufacturer, collector, researcher, or other entity. The uniqueness and universality of the identifier is useful in establishing which product in one database corresponds to which product in another database, especially across organizational boundaries.